Monitoring email deliverability ensures your emails reach inboxes, not spam folders. Here's what matters most:
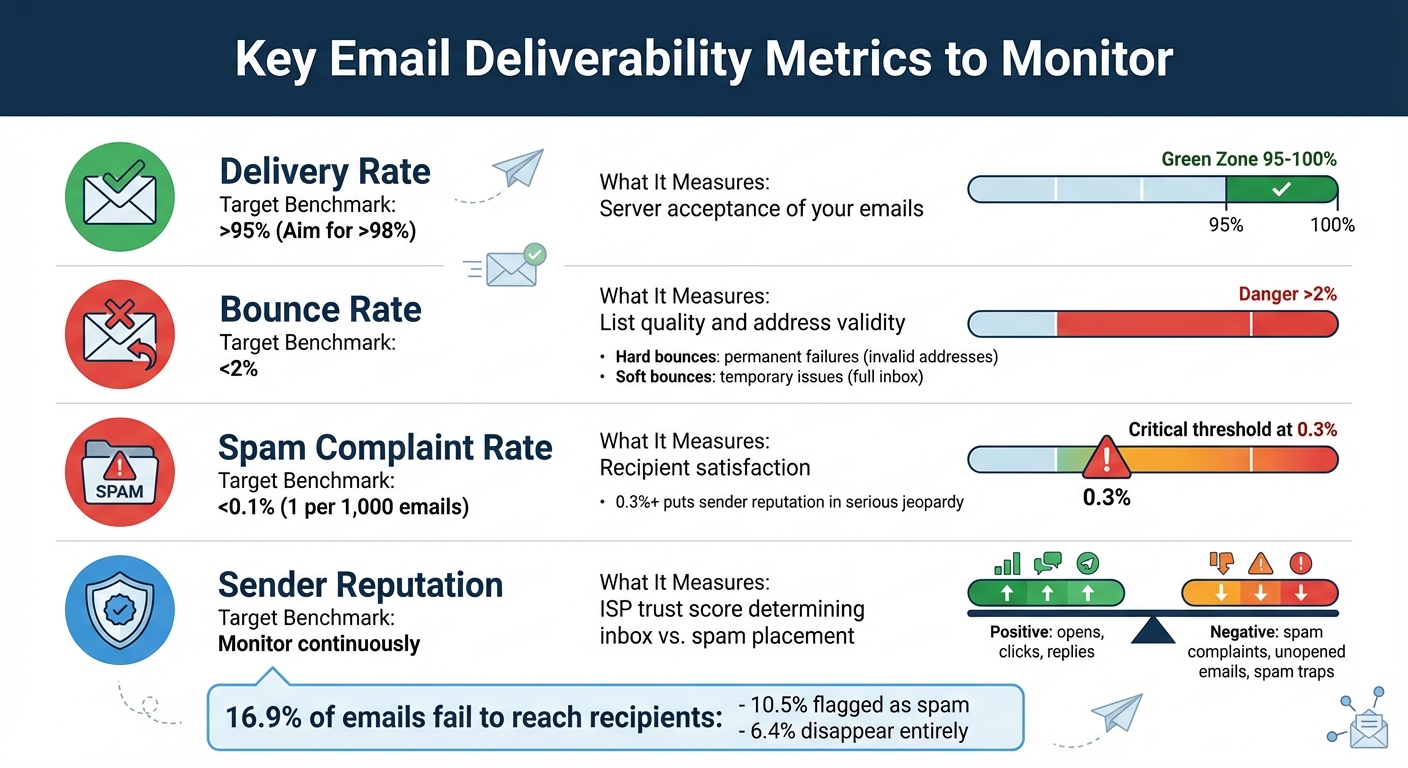
- Delivery Rate: Aim for over 95%. This shows servers accepted your emails but doesn’t guarantee inbox placement.
- Bounce Rate: Keep it under 2%. High rates signal list issues like invalid addresses.
- Spam Complaint Rate: Stay below 0.1%. Complaints harm your sender reputation.
- Sender Reputation: ISPs use this to decide if your emails land in inboxes or spam.
Why it matters: Poor deliverability can hurt your marketing ROI - emails that don’t reach inboxes waste time and money. For example, 16.9% of emails fail to reach recipients, with 10.5% flagged as spam and 6.4% disappearing entirely.
How to track: Use tools like Google Postmaster Tools, Microsoft SNDS, and SenderScore.org. Regularly clean email lists and monitor metrics daily, weekly, and monthly. Set up automated alerts for issues like bounce spikes or spam complaints.
Key takeaway: Deliverability isn’t just about sending emails; it’s about ensuring they’re seen. Proactively monitor metrics to protect your sender reputation and maximize your email marketing success.
How Do I Monitor Email Deliverability? - TheEmailToolbox.com
Key Email Deliverability Metrics to Monitor
Email Deliverability Metrics Benchmarks and Targets
Let’s break down the key email deliverability metrics that can help you identify and address potential issues before they derail your campaign. These four metrics are crucial for ensuring your emails reach their intended audience and perform effectively.
Delivery Rate
The delivery rate represents the percentage of emails successfully accepted by the recipient's server. To calculate it, divide the number of delivered emails by the total sent, then multiply by 100. For example, if you send 10,000 emails and 9,800 are accepted, your delivery rate is 98%. Ideally, you want this rate to be above 95%, with 98% or higher being the gold standard. Keep in mind, though, that this metric only tracks whether the server accepted your email - it doesn’t guarantee it landed in the inbox.
Bounce Rate
Your bounce rate shows the percentage of emails that failed to get delivered. A bounce rate below 2% is essential, as anything higher signals list hygiene problems that could hurt your sender reputation. Bounces fall into two categories:
- Hard bounces: These are permanent failures caused by reasons like invalid email addresses, typos, or non-existent domains. You should remove these addresses immediately.
- Soft bounces: These are temporary issues, such as full inboxes or server downtime. These emails may be retried before being flagged as undeliverable.
For instance, if you send 10,000 emails and 150 bounce, your bounce rate is 1.5%. Since email lists can degrade by 25–30% annually due to job changes or abandoned accounts, regular list cleaning is a must.
Spam Complaint Rate
The spam complaint rate measures how often recipients mark your emails as spam. You calculate it by dividing the number of spam complaints by the total emails sent. For example, if 5 out of 10,000 recipients flag your email as spam, your complaint rate is 0.05%. To stay on the safe side, aim for a spam complaint rate below 0.1% - that’s roughly 1 complaint per 1,000 emails. A rate of 0.3% or higher puts your sender reputation in serious jeopardy. Common causes of spam complaints include misleading subject lines, excessive email frequency, or reaching out to people who didn’t explicitly opt in. To address this, make sure your unsubscribe link is easy to find and promptly honor any opt-out requests.
Sender Reputation
Your sender reputation is like a trust score that internet service providers (ISPs) use to decide whether your emails land in the inbox or the spam folder. ISPs evaluate factors like your sending history, engagement rates, and spam complaints. Tools like Google Postmaster Tools (for Gmail) and Microsoft SNDS (for Outlook and Hotmail) can help you monitor your reputation. Positive engagement - such as opens, clicks, and replies - boosts your reputation. On the flip side, spam complaints, unopened emails, and spam traps can harm it. If your reputation takes a hit, recovery can take weeks or even months, so regular monitoring and proactive steps are critical.
Here’s a quick summary of these metrics and their benchmarks:
| Metric | Target Benchmark | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Rate | >95% (Aim for >98%) | Server acceptance of your emails |
| Bounce Rate | <2% | List quality and address validity |
| Spam Complaint Rate | <0.1% | Recipient satisfaction |
Tools for Monitoring Email Deliverability Metrics
Keeping tabs on email deliverability is essential, and monitoring tools can help ensure your emails are hitting inboxes as intended. Using a combination of free and paid tools gives you a clearer picture of your email health and provides ongoing insights to improve performance.
Free Monitoring Tools
Start with Google Postmaster Tools (GPT). Since it pulls data straight from Google, it's the most reliable source for Gmail-specific insights. GPT shows your domain and IP reputation, spam complaint rates, and whether your authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) are set up correctly. To use it, you'll need to verify your domain ownership by adding a TXT or CNAME record via your DNS provider (like GoDaddy or Namecheap). Keep in mind that GPT requires a minimum of 100–300 daily emails sent to Gmail addresses to generate data. Considering Gmail often makes up around 60% of email lists for U.S.-based businesses, focusing on Gmail performance can give you a solid grasp of overall deliverability.
For Outlook and Hotmail users, Microsoft Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) offers similar insights. SNDS provides a straightforward "Green/Yellow/Red" reputation system and tracks spam trap hits, but it's only available for dedicated IP senders.
Other free options include:
- SenderScore.org: Assigns a reputation score (0–100) to your IP address based on data from various mailbox providers, though it excludes Gmail, Microsoft, and Yahoo.
- Mail-tester.com: Checks your email's authentication and content for potential issues before you send.
- MXToolbox: Monitors whether your domain or IP has been added to any blocklists.
Once you've covered the basics with these tools, consider upgrading to paid solutions for deeper insights and automation.
Paid Monitoring Tools
Paid tools go beyond the basics, offering advanced features like automation and real-time alerts. Seed testing services such as GlockApps and SendForensics use dedicated test addresses to check inbox placement across providers. This is critical because bounce reports alone won't tell you if an email that was "accepted" ended up in a spam folder.
Some standout paid options include:
- SendForensics and MailGenius: These tools offer real-time alerts for reputation changes, DMARC monitoring to catch authentication issues, and content analysis to flag potential spam triggers.
- Bouncer: Focuses on cleaning your email list by removing invalid addresses, duplicates, and spam traps before sending.
- Litmus: Analyzes your email's HTML, checks for broken links, and evaluates your image-to-text ratio to prevent content-related deliverability problems.
"One of the essential tools in email deliverability is Google Postmaster Tools. It contains data straight from Gmail, making it the most accurate source for metrics like complaint rates." – SendForensics Blog
The biggest advantage of paid tools is automation. They provide alerts for issues like reputation drops or spam placement, saving you from manually monitoring dashboards. Plus, they offer insights into where your emails land - whether in Gmail's "Primary" tab or the "Promotions" folder, which can significantly impact open rates.
Tool Comparison
Here's a quick breakdown of free and paid tools, highlighting their strengths and limitations:
| Tool | Primary Focus | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Postmaster Tools | Domain & IP Reputation | Gmail, Google Workspace | Requires 100+ daily emails |
| Microsoft SNDS | IP Reputation | Outlook, Hotmail, MSN | Only for dedicated IPs |
| SenderScore.org | IP Health Score | General IP reputation | Excludes Gmail, Microsoft, Yahoo |
| Mail-tester.com | Content & Authentication | Pre-send troubleshooting | No long-term tracking |
| MXToolbox | Blocklists | Blocklist status | Manual checks without alerts |
| GlockApps | Seed Testing | Inbox vs. spam placement | No real user engagement simulation |
| SendForensics | Infrastructure & Content | DMARC monitoring, alerts | Paid service |
| Bouncer | List Hygiene | Bulk email verification | Paid service |
For most businesses, starting with Google Postmaster Tools is a logical first step since it’s free and covers a large portion of your email list. If you rely on a dedicated IP and send to a significant number of Outlook users, adding Microsoft SNDS can be helpful. Paid tools like seed testing or content analysis scanners can then be layered in as your budget and email campaigns grow in complexity.
sbb-itb-a84ebc4
Setting Up a Monitoring Routine
Once you've chosen your tools, the next step is to establish a regular monitoring routine. Divide your tasks into daily, weekly, and monthly categories based on their urgency and impact.
Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Monitoring Tasks
Daily monitoring is all about addressing immediate issues. Keep an eye on delivery rates, bounce spikes, and 4xx/5xx server errors - these could signal technical problems. Spam complaints should stay under 0.1%, as exceeding this threshold can harm your sender reputation. If you send transactional emails, like password resets or order confirmations, monitor them separately from your marketing campaigns since these messages directly affect user trust.
Weekly tasks focus on spotting trends. Compare your weekly performance against benchmarks. A sudden drop in open rates or a dip in your sender reputation score could mean your emails are landing in spam folders. Use tools like Google Postmaster Tools or SenderScore.org to check your IP and domain reputation weekly. This cadence helps you identify patterns without waiting too long, ensuring problems don’t escalate.
Monthly audits are for deeper maintenance. While hard bounces should be removed after each campaign, dedicate time each month for thorough list hygiene. Remove inactive subscribers who haven’t engaged in over 90 days and run bulk verifications to catch spam traps. Confirm that your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records are correctly configured, especially if you've made DNS changes or switched email providers. About 60% of senders clean their lists monthly, understanding that 25–30% of email addresses can become invalid annually due to job changes or abandoned accounts.
Here’s a quick summary of these tasks:
| Frequency | Task | Key Metrics/Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Delivery & Error Check | Monitor delivery rates, 4xx/5xx errors, and bounce spikes |
| Daily | Complaint Monitoring | Keep spam complaints below 0.1% |
| Weekly | Trend Analysis | Compare against benchmarks; check sender reputation scores |
| Weekly | Reputation Review | Use Google Postmaster or SenderScore to evaluate IP/domain reputation |
| Monthly | List Hygiene | Remove inactive subscribers and verify email lists |
| Monthly | Security Audit | Confirm SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configurations |
| Monthly | Spam Trap Scan | Identify recycled or pristine spam traps |
Configuring Automated Alerts
Routine checks are essential, but automated alerts can catch critical issues as they happen. Set threshold-based notifications for key metrics, like bounce rates exceeding 2% or spam complaints rising above 0.1%. These alerts serve as early warning systems, helping you address problems before they harm your reputation.
If your email service supports event webhooks, use them. Webhooks push real-time data - such as bounces, clicks, and spam reports - directly to your system, enabling immediate action instead of relying on delayed batch reports. For blacklist monitoring, tools like MXToolbox can notify you if your IP or domain appears on a blocklist, giving you time to resolve the issue before it impacts your deliverability across providers.
Authentication failures also require special attention. Set alerts for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC failures, as these can indicate spoofing attempts or configuration errors that could harm your reputation. Additionally, establish internal SLAs to define normal performance metrics for your campaigns. For instance, if your emails usually deliver within 5 minutes but suddenly take 30 minutes, that’s a red flag worth investigating.
"Mailbox providers never intentionally filter or block legitimate email that users ask for, but due to the sheer volume of spam... sometimes wanted email gets caught within the cross-hairs. This is why it's so crucial that all senders track inbox placement rates in addition to delivery rates." – Brad Van der Woerd, Head of Customer Success, Inbox Monster
Analyzing Trends and Taking Action
Spotting Patterns in Deliverability Metrics
To identify potential issues in deliverability, start by comparing your current metrics with both historical data and industry standards. For instance, if your delivery rate typically hovers around 96% but suddenly dips to 88%, that’s a clear sign something has shifted - even though 88% might not seem alarming on its own.
Separate your email types - transactional versus marketing - and monitor them individually. For example, if marketing email open rates drop while transactional emails remain stable, the issue is likely tied to content rather than technical settings. Similarly, track performance across major ISPs such as Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook separately. If Gmail users show a sharp decline in open rates while Yahoo users don’t, it could indicate a reputation issue specific to Google.
Open rates can serve as an indirect indicator of inbox placement. A sudden drop in open rates, even when delivery rates remain high, might suggest that spam filters are flagging your emails. Pay attention to the balance between positive signals (like opens, clicks, replies, and forwards) and negative signals (such as spam complaints, unsubscribes, and deletes without opening). This ratio can provide valuable insight into the overall health of your sender reputation.
To pinpoint issues more effectively, segment your campaigns. By isolating specific variables, you can better understand what’s causing changes and take appropriate action.
Fixing Common Issues
Once you’ve identified the problems, here’s how to address them. Start by verifying your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configurations. Make sure SPF records stay within the 10-DNS lookup limit, and use DKIM keys that are at least 1,024-bit. If your bounce rate exceeds 2%, it’s a clear sign of poor list hygiene. Remove hard bounces immediately and implement a double opt-in process for new subscribers. For spam complaints exceeding 0.1%, make your unsubscribe link more prominent and review your email content for spam triggers like excessive capital letters, too many fonts, or an unbalanced text-to-image ratio.
Maintaining a strong sender reputation is crucial. If you need to recover from a poor reputation, pause non-essential email campaigns for a week. Then, gradually resume sending - starting with your most engaged users. Build trust over an 8-week period by increasing volume slowly. If you're transitioning to a new IP or recovering from a major issue, warm up the IP gradually. Begin with 50-100 emails on the first day and double the volume every few days, focusing exclusively on your most engaged recipients. Regularly monitor blacklists using tools like MXToolbox, and if you find your domain or IP listed, follow the necessary removal steps.
"A reply is the gold standard of email engagement. When someone replies to your email, it's the strongest positive signal you can get." – Yaroslav Hurchenko, Email Deliverability Expert, Mailtrap
Conclusion
Keeping a close eye on email deliverability metrics is crucial for successful email marketing. Laura Sullivan, Head of Brand and Marketing at Inbox Monster, captures it perfectly:
"Delivery is table stakes. Deliverability is what drives results".
A high delivery rate doesn’t mean much if your emails end up in spam folders. In fact, about 16.9% of all emails fail to reach the intended inbox - 10.5% land in spam, while 6.4% vanish entirely.
To stay ahead, establish a consistent monitoring routine. Use the right tools and set up automated alerts to flag problems like sudden spikes in bounce rates or blacklist appearances. These alerts help you act quickly and prevent damage to your sender reputation. Remember, tracking inbox placement - not just delivery - is key. Keep an eye on critical metrics and act promptly when issues arise.
Authentication failures, blacklist listings, and poor list hygiene can snowball into major problems if ignored. Address them immediately to avoid permanent blocks. It’s worth the effort - email marketing still offers an impressive return of $36 for every $1 spent , but only if your emails actually make it to the inbox.
Protecting your sender reputation is an ongoing process, much like maintaining a credit score with ISPs. Make monitoring a regular habit, not an afterthought. With a proactive approach, you can maximize your ROI and ensure your emails consistently land where they belong: in your subscribers' primary inbox.
FAQs
What are the best tools to track email deliverability metrics?
Monitoring email deliverability is a crucial step in making sure your messages land in your audience's inbox rather than getting lost in spam folders. Some powerful tools to help with this include Litmus’s Email Guardian, which keeps tabs on sender authentication and reputation, Google Postmaster Tools and Microsoft SNDS, both offering detailed insights directly from mailbox providers, and MailGenius, which tests inbox placement and flags potential issues.
By using these tools, you can track important metrics like bounce rates, spam complaints, and inbox placement. Regularly analyzing this data allows you to fine-tune your email campaigns, enhance deliverability, and ultimately boost overall email performance.
What steps can I take to fix a damaged sender reputation?
To fix a damaged sender reputation, start by cleaning up your email list. This means removing hard bounces, inactive users, and unengaged email addresses. Next, ensure your domain is properly authenticated using SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols - these help build trust with email providers. If you're working with new or low-volume IPs, warm them up gradually to create a positive sending history.
Send relevant, permission-based emails that encourage engagement, like opens and clicks, while steering clear of spam-like behaviors. Keep an eye on blocklists, feedback loops, and spam complaint rates, and address any problems quickly to maintain or rebuild your reputation over time.
What should I do if my email bounce rate is over 2%?
If your email bounce rate crosses 2%, you need to take action fast to safeguard your sender reputation. Start by cleaning up your email list - remove hard bounces and invalid addresses. To prevent future issues, consider using email verification tools or setting up a double opt-in process to confirm the accuracy of new contacts.
Keep an eye on soft bounces as well, which might indicate temporary problems like full inboxes or server glitches. In these cases, try re-sending the email after a short wait. By regularly managing your email list and tracking bounce rates, you can boost deliverability and ensure more of your emails land in your audience's inbox.


