Legal risks in attribution tools are real, but compliance can protect your business and build user trust. Here’s what you need to know:
- Regulations vary by region: GDPR (EU) requires opt-in consent, while CCPA (California) follows an opt-out model. By 2026, 20 U.S. states will have privacy laws.
- Non-compliance is costly: GDPR fines have exceeded €2 billion, and CCPA violations can cost up to $7,988 per intentional breach.
- Privacy tools help: Google Consent Mode can recover 70% of lost conversion data while maintaining compliance.
- AI regulations are coming: The EU AI Act (effective August 2, 2026) mandates clear labeling for AI-generated content.
To stay compliant, map customer locations, audit your data collection methods, and implement privacy-focused tracking systems. Regular monitoring and detailed documentation are essential to avoid fines and maintain trust. For more on scaling your operations safely, explore our marketing funnel insights.
Improve Marketing Attribution with Effective Consent Management : Google Analytics Tutorial
sbb-itb-a84ebc4
Identify the Regulations That Apply to Your Business
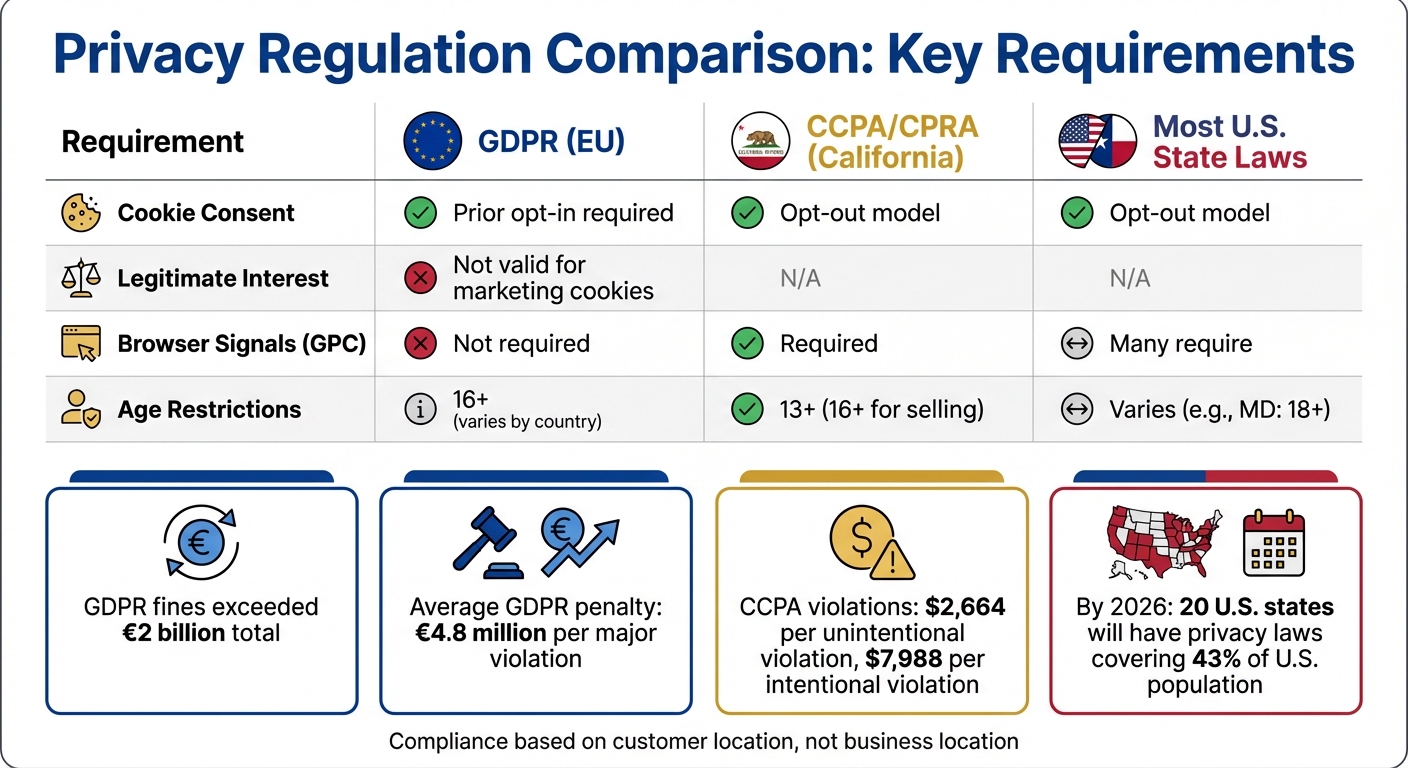
GDPR vs CCPA vs US State Privacy Laws Compliance Requirements Comparison
Major Compliance Frameworks and Their Requirements
If your business uses attribution tools, you’ll need to navigate a maze of regulations that depend on where your customers live and the industry you operate in. For example, GDPR applies to any company handling the data of EU residents, requiring prior opt-in consent for marketing cookies and tracking. This rule applies regardless of your company's location. By 2025, GDPR fines had surpassed €2 billion, with an average penalty of €4.8 million per major violation.
In the U.S., CCPA and CPRA take a different approach, relying on an opt-out model. Businesses in California must honor browser-based signals like Global Privacy Control (GPC) and provide clear "Do Not Sell/Share" options. As of December 31, 2024, California eliminated its 30-day cure period, meaning violations now face immediate fines - $2,664 per unintentional violation and $7,988 per intentional violation. By 2026, 20 states will have comprehensive privacy laws, covering about 43% of the U.S. population. States like Indiana, Kentucky, and Rhode Island will join this framework on January 1, 2026, with Rhode Island notably offering no cure period for violations.
Certain industries face additional rules. HIPAA applies to healthcare entities, with updates to the Security Rule expected by late 2025 or early 2026, likely requiring multi-factor authentication and stronger encryption. Financial institutions must follow GLBA, which carries fines of up to $100,000 per offense. Meanwhile, the EU AI Act will fully take effect on August 2, 2026, requiring companies to classify AI systems into four risk levels and maintain detailed documentation for high-risk systems.
| Requirement | GDPR (EU) | CCPA/CPRA (California) | Most U.S. State Laws |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cookie Consent | Prior opt-in required | Opt-out model | Opt-out model |
| Legitimate Interest | Not valid for marketing cookies | N/A | N/A |
| Browser Signals (GPC) | Not required | Required | Many require |
| Age Restrictions | 16+ (varies by country) | 13+ (16+ for selling) | Varies (e.g., MD: 18+) |
How to Determine Which Regulations Apply to You
Once you’re familiar with the major frameworks, it’s time to figure out which ones apply to your business. Start by mapping out where your customers are located to build a profitable online business - privacy laws are based on your customers’ residence, not your company’s location. For instance, if you serve California or EU residents, you’ll need to comply with CCPA or GDPR, respectively.
Next, consider your industry and the types of data you handle. If you work in healthcare and manage Protected Health Information, you’ll need to follow HIPAA. Financial institutions are subject to GLBA and SOX, while retailers processing credit card payments must comply with PCI-DSS. If your business uses AI for profiling or automated decisions, keep in mind that the EU AI Act will apply to high-risk applications starting August 2, 2026.
To stay compliant, map customer locations, review industry-specific requirements, and conduct an annual compliance review. This process should include assigning a compliance officer to inventory tracking technologies, document data flows, and identify relevant laws. With 86% of U.S. consumers expressing growing concerns about data privacy, adopting a "highest common denominator" approach can simplify operations. By following the strictest standards, like GDPR and CCPA, you can prepare for future regulations and streamline your compliance efforts globally.
Review Your Current Data Collection Setup
Building a compliant attribution system requires reliable tracking tools and consistent, high-quality data. Start by examining how your current attribution tools collect and manage data. This step is critical because 51% of CTOs and chief data officers distrust the data they receive from marketing platforms, and broken tracking systems lead to over $66 billion in wasted marketing spend every year.
Assess Your Tracking Tools and Infrastructure
Take stock of every data element your attribution tools handle. This includes identifying the types of data collected, their sources, how they’re processed, and where they’re stored. Be thorough - review all tools in your stack, from CRMs and email platforms to Google Tag Manager and Meta Pixel.
This detailed categorization is vital for managing user consent. With 40% of users declining cookies when provided with clear options, you need to pinpoint which tools will lose functionality when consent is withheld.
Also, evaluate third-party vendors. Investigate their data handling practices to ensure compliance. Check for built-in privacy features like Facebook's "Limited Data Use" tool, which limits how user data is processed. Additionally, test your consent banners and optimize your conversion rates to confirm they avoid manipulative designs that might compromise user trust.
If browser restrictions are hampering your data collection, consider server-side tracking. This approach offers more control over your data and helps circumvent browser limitations.
Once your tools and vendor compliance are mapped out, the next step is to verify the quality and consistency of your data.
Check Data Quality and Consistency
After cataloging your tracking setup, focus on ensuring your data’s accuracy. Poor data quality can undermine your efforts, especially when 47% of marketing budgets are wasted due to flawed attribution systems. Even with compliant tools, inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to unreliable insights and poor decision-making.
Look for and resolve common issues like duplicate records, missing fields, or inconsistent event naming. These problems often arise from "control drift", where systems evolve over time, but compliance settings and data structures remain outdated.
Automating data cleaning and validation can help catch errors and maintain standardized data. Use version control and validation rules to ensure your data schemas stay consistent as you integrate new campaigns or tools.
Conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) to pinpoint risks in your data flows. This involves examining how personal data moves through your attribution system and identifying vulnerabilities in areas like logging, monitoring, access controls, and vendor management [34]. While privacy-focused measurement may reduce attribution accuracy by 10-20%, it significantly lowers compliance risks.
Set Up Privacy-Compliant Tracking Systems
Once you've reviewed your data setup, the next step is configuring tracking tools that respect user privacy while ensuring accurate data measurement. This involves adapting your systems in real time based on user consent choices and integrating marketing funnel tools to meet compliance standards.
How to Configure Compliant Tracking Tools
To ensure compliance and maintain accurate attribution, server-side tracking is a must. Using server-side Google Tag Manager (GTM), you can reduce reliance on cookies, bypass ad blockers, and control the flow of data to vendors [39]. Start by configuring the server_container_url parameter in your client-side Google Tag and setting the first_party_collection flag to "true" [39].
For platforms like Facebook, leverage Meta CAPI with the Facebook Pixel. To avoid double-counting, ensure you send matching event_id values [39]. Map your GA4 field names to Meta parameters - for example, user_data.email_address corresponds to em, and x-fb-ck-fbc maps to fbc [39].
Google Consent Mode v2 is another critical tool. It adjusts tag behavior based on real-time consent, allowing you to model conversions even when users reject cookies. According to Google, conversion modeling can recover up to 70% of ad-click-to-conversion paths that would otherwise be lost due to cookie rejections. Ensure your default consent state is set to "denied" for all non-essential purposes until explicit user consent is received.
After setting everything up, validate your configuration using GTM Preview mode. Check the "Outgoing HTTP Requests" from the server container to confirm that the status is "200" and that sensitive data is only transmitted when the relevant consent signals are present [39].
Add Consent Management Systems
With your tracking tools in place, the next step is integrating a Consent Management Platform (CMP) to handle user choices seamlessly. This process involves three key steps: collecting user consent through a banner, communicating their preferences to tracking providers like Google, and ensuring tags behave accordingly [42].
Google Consent Mode offers two implementation options. In Basic mode, tags are completely blocked until consent is granted, meaning no data is sent beforehand. In Advanced mode, tags load with a "denied" default and send "cookieless pings" for conversion modeling until consent is provided [42]. Advanced mode is particularly useful for advertisers seeking detailed modeling while adhering to privacy rules [42].
Your CMP should support various consent types, including ad_storage for advertising cookies, ad_user_data for sending user data to Google, ad_personalization for remarketing, and analytics_storage for analytics tracking [42]. Use APIs and webhooks for real-time synchronization, ensuring consent changes are instantly applied across your marketing tools.
If a user withdraws consent, activate ads_data_redaction to remove any stored identifiers [42]. This aligns with the principle that withdrawing consent should be as simple as granting it, giving users the ability to update their preferences anytime.
Meet AI Transparency and Disclosure Requirements
With AI becoming a core part of attribution tools, new disclosure rules are set to take effect on August 2, 2026. These rules apply to tools that use AI for tasks like modeling conversions, generating creative content, or suggesting budget allocations. If AI plays a role in your attribution process, you’ll need to clearly disclose its involvement.
How to Disclose AI-Generated Content
By 2026, two layers of disclosure will be mandatory: one for users and one for machines.
- Visible disclosure for users: This includes captions, watermarks, or the widely recognized "cr" icon placed on AI-generated images [51].
- Embedded metadata for machines: Using the C2PA (Content Authenticity Initiative) standard, metadata must include details like Provider Name, System Version, Creation Timestamp, and a Unique Identifier [51].
"The goal isn't to prevent use of AI but rather to inform website users of the use of AI." - Cookie-Script Guide [51]
For text-based outputs, such as attribution reports or AI-generated insights, make disclosures prominent by placing them at the beginning or end of the document in plain, straightforward language. For example, use wording like: "This recommendation was generated by AI and reviewed by our team." Avoid hiding these disclosures in footers or on separate pages where users might miss them [51][57].
Important Note: Never use screenshots of AI-generated images in dashboards or marketing materials. Screenshots strip the required C2PA metadata, making the files non-compliant [51]. Always use the original file to retain compliance.
Your attribution tool must also prioritize clarity. Replace opaque "black-box" AI scores with clear explanations, such as: "Search drove 41% of assisted revenue via last-click and time-decay weighting." Transparency is critical: 71% of customers expect companies to be upfront about their AI usage, and 75% of business leaders believe a lack of transparency could lead to customer churn [49].
These practices not only ensure compliance but also build trust with users.
Prepare for EU AI Act Article 50
The EU AI Act Article 50 will become enforceable on August 2, 2026 [50][51]. This regulation requires that AI-generated outputs be both machine-readable and clearly identifiable. For attribution tools, this means any AI-generated content - whether deepfakes, synthetic images in ads, or text on public topics - must be labeled unless reviewed and edited by a human [50][51].
| Region | Effective Date | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | August 2, 2026 | Machine-readable labels; clear deepfake identification [51][50] |
| California (US) | August 2, 2026 | Tamper-proof labels for images, video, and audio [51] |
| China | September 1, 2025 | "AI" symbol/watermark required; chatbot disclosures [51] |
Failure to comply could result in hefty penalties - up to 3% of global annual revenue or €15 million under the EU AI Act [58][51]. In some regions, fines in the tens of millions have been proposed for failing to label AI-generated content [49].
To stay ahead, keep time-stamped audit logs of model versions, data inputs, and decision-making processes [49][55]. These records are essential for regulatory reviews and proving that your tool operates transparently.
Additionally, set up a change management protocol to review disclosure documentation whenever AI models are updated [58]. For major decisions, integrate a human-in-the-loop review to ensure manual approval before implementing significant financial changes [49].
Monitor and Document Compliance Over Time
Staying compliant isn’t a one-and-done task - it requires constant monitoring and meticulous record-keeping. As regulations shift and your attribution tools evolve, you need systems that can adapt, track compliance, and provide proof during audits.
Use Monitoring Tools to Track Compliance
Real-time monitoring tools are your first line of defense against potential compliance issues. Platforms like IBM watsonx.governance, ServiceNow AI Control Tower, and Microsoft Responsible AI act as centralized hubs for overseeing AI-driven attribution models. These tools help ensure adherence to regulations such as the EU AI Act and create audit trails, even when working across cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or IBM [64].
For technical checks, tools like the Attribution Reporting Header Validator are invaluable for verifying API registration headers [61][62]. Developers can also use Chrome’s built-in interface (chrome://attribution-internals/) to inspect sources, triggers, and scheduled reports directly on their devices. Debug reports, whether in "attribution-success" or "verbose" mode, are handy for troubleshooting configurations and comparing privacy-preserving attribution results to older, cookie-based methods [61][63].
To avoid compliance risks from data drift, tools like Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor can flag issues like training-serving skew or inference drift, which might affect the accuracy of your attribution models [64]. Monthly consent rate reviews and quarterly deep dives into attribution models, policy settings, and regulatory updates are also key to staying ahead [68].
Keep Records and Audit Trails
Monitoring is only part of the equation - detailed logs are essential for audits. Document user actions with timestamps, action types, and outcomes [65][67]. Your system should also log changes to critical elements like attribution instances, datasets, schemas, access controls, and segment activations [65][67].
Since many platforms only retain logs for 365 days, it’s important to export audit logs regularly to a secure location [65][67]. APIs can help pull complete audit data, as UI-based logs often have limited lookback windows - usually 90 days or 1,000 events [65]. For attribution-specific audits, maintain a comparison table that tracks metrics like last-click share, platform-reported contributions, and data-driven shares. This can help you spot shifts after configuration updates [68].
To provide full context during regulatory reviews, your audit system should capture before-and-after states of all changes, including previous and current values [67]. Keep time-stamped logs of model versions, data inputs, and decisions to demonstrate transparency. Automating alerts for high-risk actions, like dataset deletions, adds another layer of security [65].
"Transparent documentation enhances audit efficiency and speeds response to market shifts." - Gabrielle Thomson, Customer Science [68]
Conclusion
Ensuring compliance in attribution tools isn’t a one-and-done task - it’s an ongoing process that requires careful attention, thorough documentation, and strong resources. By following key steps like identifying relevant regulations, auditing your data collection methods, using privacy-compliant tracking, meeting AI transparency standards, and keeping up with continuous monitoring, you can build a solid framework that protects your business and your customers alike. This approach not only secures data integrity but also strengthens regulatory compliance and customer trust.
The stakes are high when it comes to regulatory risks. For instance, violations of GDPR can lead to fines as steep as €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, while under the CCPA, penalties can hit $7,500 per intentional violation [73]. Beyond the financial repercussions, there’s the issue of public perception - 79% of Americans express concern about how companies handle their data. A failure to comply can lead to immediate and often irreversible damage to customer trust.
Adopting privacy-first attribution may reduce accuracy by 10–20%, but it also significantly lowers compliance risks. When you weigh this trade-off against the long-term advantages - like sustainable measurement practices and a stronger brand reputation - it’s clear that the benefits far outweigh the costs.
FAQs
How can I figure out which privacy laws apply to my business?
To figure out which privacy laws apply to your business, start by looking at three key factors: where your business operates, where your customers are located, and the type of data you collect. For instance, if you handle data from residents of the European Union, you’ll need to comply with the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) - even if your business isn’t based in Europe. Similarly, if your business operates in California or serves its residents, you must adhere to the CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) and its successor, the CPRA.
In the U.S., state-level privacy laws are becoming more common, with new regulations rolling out in the coming years. If your business serves customers in multiple states or internationally, you might also face requirements from global laws modeled after GDPR. To stay compliant, it’s smart to map out how data flows through your business and consult legal experts to ensure you’re following all relevant regulations.
How can I make sure my attribution tools comply with GDPR and CCPA regulations?
To make sure your attribution tools align with GDPR and CCPA requirements, start by familiarizing yourself with how these regulations define and protect personal data. This includes details like cookies, device IDs, and user IDs, which often require explicit user consent for tracking and processing.
Create a transparent data governance framework that prioritizes clear and informed user consent, especially in areas where cookie consent is legally required. Shift your focus to first-party data and adopt privacy-friendly methods like aggregated measurement and consent-based frameworks to adapt to the growing emphasis on user privacy.
It's also crucial to regularly audit your attribution tools to ensure compliance as privacy laws and technologies continue to evolve. Taking a proactive approach will not only keep you compliant but also allow you to maintain effective marketing strategies in an ever-changing privacy landscape.
How could upcoming AI regulations affect my business's data practices?
AI regulations are evolving, and they're changing how businesses manage data, particularly in marketing and attribution. Laws like the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) and global frameworks such as GDPR focus on three key principles: transparency, user consent, and responsible data usage. For example, companies may now be required to obtain clear, explicit opt-in consent for tracking activities and offer straightforward explanations for AI-driven decisions.
To navigate these changes, businesses should prioritize privacy-first strategies. This includes relying on first-party data and adopting privacy-preserving attribution models. Not only do these approaches align with legal requirements, but they also help foster trust with customers - a crucial factor in today’s data-conscious world.
Being proactive and staying updated on regulatory developments is essential. This helps ensure compliance, avoid potential penalties, and maintain effective marketing strategies in an increasingly regulated environment.


